Bile Duct Cancer
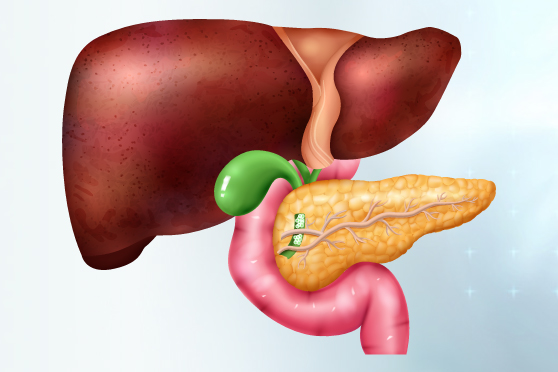
What is bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma)?
Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a type of cancer that affects the tubes (ducts) that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and intestines. Bile is a fluid that helps in the digestion of food. Bile duct cancer occurs when malignant (cancerous) tumors form in these ducts.
Types of bile duct cancer
- Intrahepatic bile duct cancer: This type of cancer forms on the bile ducts inside the liver.
- Extrahepatic bile duct cancer: This type forms on the bile ducts outside the liver and is the most common form. There are two forms of extrahepatic bile duct cancer:
A. Perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: It occurs in the area where the right and left bile ducts exit the liver to form a common bile duct.
B. Distal cholangiocarcinoma: It is located in the distal region where the common bile duct passes through the pancreas and enters the small intestines.
Risk factors
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC): A condition that causes scarring or inflammation leading to the blockage of bile ducts.
Bile duct cysts: Blockage of the bile ducts due to cysts, causing swelling, inflammation, and infections.
Chronic ulcerative colitis: Damage to the large intestines due to sores, ulcers, and inflammation.
Germline mutations: Inherited genetic changes.
The symptoms of bile duct cancer may include:
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes)
Dark urine
Clay-colored stool
Abdominal pain
Chills

Fever
Itchy skin (pruritus)
Nausea and vomiting
Unexplained weight loss
Loss of appetite
Diagnosis
To diagnose bile duct cancer and determine its stage, the following tests and procedures may be performed:
- Physical exam and health history
- Liver function tests
- Laboratory tests
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and CA 19-9 tumor marker tests
- Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, MRCP)
- Biopsy (removal of cells or tissues for microscopic examination)
Treatment
The treatment options for bile duct cancer depend on various factors, such as the cancer's location, stage, and overall health of the patient. The main treatment approaches include
Surgery
Systemic therapy

Liver transplant
Clinical trials
Clinical trials are research studies that test new medical approaches in people. They aim to find safe and effective ways to prevent, diagnose, or treat diseases. Participating in clinical trials may be an option for those with cholangiocarcinoma. Consult with your physician for more information.
Questions to ask your doctor
If you have bile duct cancer, you may want to ask your doctor the following questions
- Is the cancer only in my bile ducts?
- Do I need further testing before considering treatment options?
- Will genetic testing be beneficial?
- Are you experienced in treating this type of cancer?
- Do I need to see any other specialists?
- How much experience do you have in treating this type of cancer?
- Can surgery remove the cancer?
- What are the goals of treatment?
- What are the common side effects of the recommended treatment? How long do they typically last?
- How quickly do we need to decide on treatment?
- How long will the treatment last? What will it be like? Where will it be done?
- How will treatment affect my daily activities?
- What are the chances of curing the cancer with the recommended treatment?
- What are the options if the treatment doesn't work or if the cancer comes back?
- What type of follow-up care will be needed?
- Will genetic testing be beneficial for my treatment plan?










